MicroPython
Python for micro-controllers.
Contents
What is MicroPython?
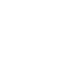 micropython.org
micropython.org
“MicroPython is a lean and efficient implementation of the Python 3 programming language that includes a small subset of the Python standard library and is optimised to run on microcontrollers and in constrained environments.”
Compiler vs Interpreter
Hardware
Supported Devices
This Presentation
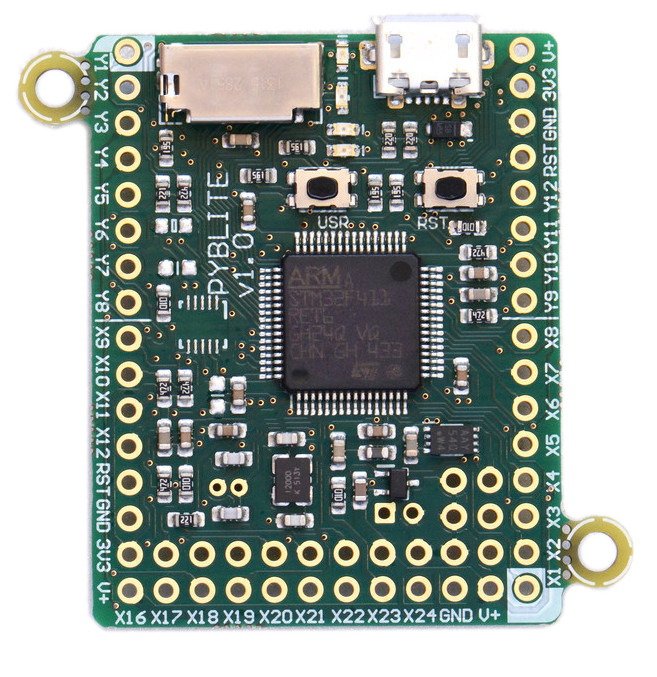
pyboard v1.1
For the rest of this presentation I'll be
using the pyboard v1.1.
Getting Started
Powering Up
- USB - also provides serial
- Power Supply - 3.5 to 10V
- Battery - 3.5 to 10V
Connect to REPL
Read Evaluate Print Loop (REPL)
$ cu -l /dev/ttyACM0
Connected.
MicroPython v1.9.2 on 2017-08-23; PYBv1.1 with STM32F405RG
Type "help()" for more information.
>>> import uos as os
>>> os.uname().version
'v1.9.2 on 2017-08-23'
for more detail: REPL tutorial
File System
Out of the Box
The pyboard's flash contains the following
flash/
README.txt
boot.py
main.py
pybcdc.inf
sd/
(sd card content)
Browse with Python
>>> import uos as os
>>> os.listdir('/')
['flash', 'sd']
>>> os.getcwd()
'/flash'
>>> os.listdir('.')
['main.py', 'pybcdc.inf', 'README.txt', 'boot.py']
Hot mount SD Card
The SD card can be mounted after boot.
>>> import uos as os, pyb
>>> os.umount('/sd')
>>> os.listdir('/')
['flash']
>>> os.mount(pyb.SD, '/sd')
>>> os.listdir('/')
['flash', 'sd']
Hot mount SD Card
RaisesOSError on failure...
import uos as os, pyb
try:
os.mount(pyb.SD, '/sd')
print("Successfully mounted SD card")
except OSError:
print("Failed to mount SD card")
Outputs
pyboard's LEDs
The pyboard has 4 LEDs onboard.| Colour | # | Pin | Pin Alias | PWM |
| red | 1 | A13 |
LED_RED |
|
| green | 2 | A14 |
LED_GREEN |
|
| yellow | 3 | A15 |
LED_YELLOW |
Yes |
| blue | 4 | B4 |
LED_BLUE |
Yes |
pyb.LED()
import pyb
red_led = pyb.LED(1)
yellow_led = pyb.LED(3)
# Basic controlls
red_led.on()
red_led.off()
red_led.toggle()
# Yellow and Blue have intensity control
yellow_led.intensity(0xff) # same as on()
yellow_led.intensity(0x00) # same as off()
Digital Outputs
Let's control the red LED directly.
import machine
# Both yield the same pin instance
pin = machine.Pin('A13', machine.Pin.OUT)
pin = machine.Pin('LED_RED', machine.Pin.OUT)
pin.names() # ['A13', 'LED_RED'] shows alternatives
# Changing pin's state
pin.high() # or: pin.on()
pin.low() # or: pin.off()
print(pin.value()) # prints 0
pin.value(1 - pin.value()) # toggles pin
PWM Output
Let's control the blue LED's intensity directly.
import machine
import pyb
pin = machine.Pin('LED_BLUE')
timer = pyb.Timer(3, freq=1000)
channel = timer.channel(1, pyb.Timer.PWM, pin=pin)
# Change blue LED's intensity manually
channel.pulse_width_percent(5)
channel.pulse_width_percent(50)
channel.pulse_width_percent(100)
Analog Output
TODOInputs
pyb.Switch()
The pyboard has a switch marked USR on board.
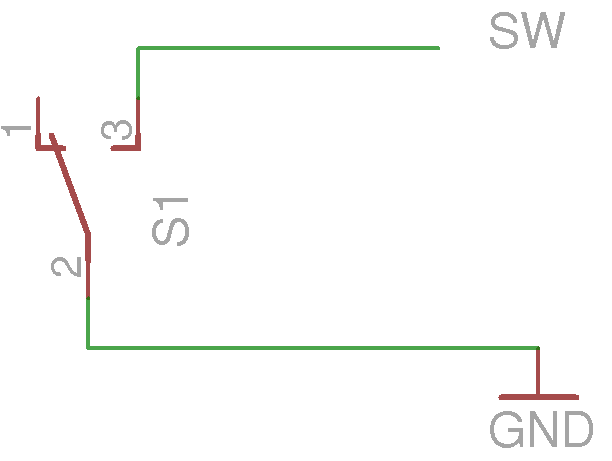
import pyb
switch = pyb.Switch()
switch.value()
# True when pressed
# False when not pressed
Digital Inputs
Check the same switch without usingpyb
import machine
# Pin connected to pyboard's Switch
pin = machine.Pin('SW')
pin.names() # ['B3', 'X17', 'SW'] alternatives
# The switch connects the B3 pin to GND when pressed
pin.value() # 0 when pressed
# 1 when not pressed
Input Pull Up/Down
Inputs can be pulled up, down, or left to float.
import machine
pin = machine.Pin('SW', machine.Pin.IN, machine.Pin.PULL_UP)
pin = machine.Pin('SW', machine.Pin.IN, machine.Pin.PULL_DOWN)
pin = machine.Pin('SW', machine.Pin.IN, machine.Pin.PULL_NONE)
# These 2 initialize the pin in the same way
pin = machine.Pin('SW') # defaults for SW are...
pin = machine.Pin('SW', machine.Pin.IN, machine.Pin.PULL_UP)
Analog Inputs
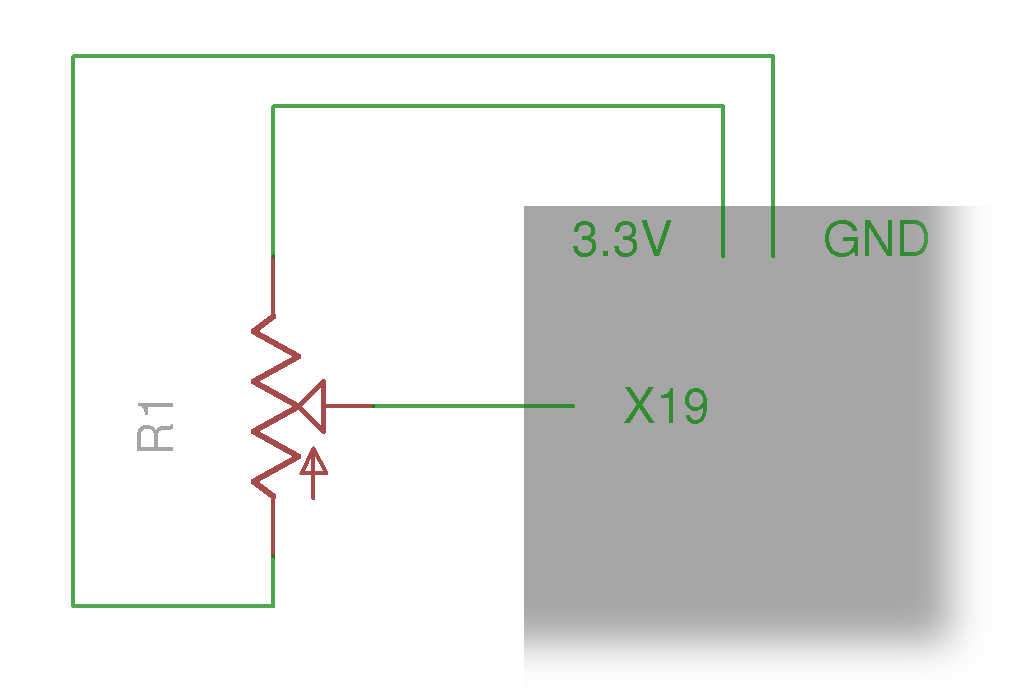
import machine
import utime as time
import pyb
pin = machine.Pin('X19')
adc = pyb.ADC(pin)
adc.read() # reads value, 0-4095
while True:
time.sleep(0.1)
value_ratio = adc.read() / 4095
print('#' * int(40 * value_ratio))
Comms
Communicationprotocols
UART
from pyb import UART
uart = UART(1)
uart.init(baudrate=9600)
uart.write(b'abc') # send 3 bytes
data = uart.read(3) # receive 3 bytes
uart.deinit()
Virtual COM Port
- UART over USB
- No wiring necessary
- baudrate can be set much higher
than standard UART
from pyb import USB_VCP
vcp = USB_VCP()
vcp.write(b'abc') # write 3 bytes
data = vcp.recv(3) # receive 3 bytes
I²C
from pyb import I2C
i2c = I2C(1) # create on bus 1
i2c = I2C(1, I2C.MASTER) # create as a master
i2c.init(I2C.MASTER, baudrate=20000) # init as a master
i2c.init(I2C.SLAVE, addr=0x42) # init as a slave
i2c.send(b'abc') # send 3 bytes
i2c.send(0x42) # send a single byte
data = i2c.recv(3) # receive 3 bytes
i2c.deinit() # turn off the peripheral
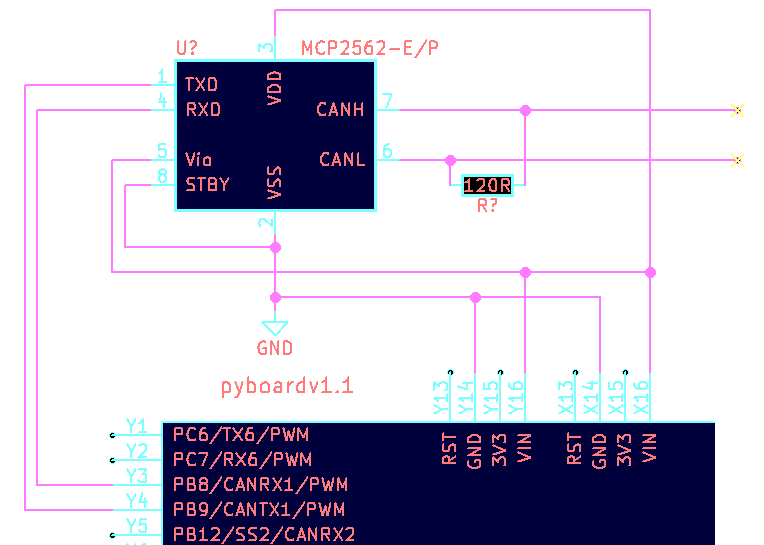
Controller Area Network (CAN)
- Used in all modern cars
- Excellent immunity to noise
- Large distances: 40m, even up to 1km
- pyboard has 2 CAN controllers
- Requires a tranceiver (probably:
MCP2562)
CAN: Wiring Diagram
CAN: Bit timing
1-bit
$prescaler = \frac{pclk1}{baud \times (1+bs1+bs2)}$
import pyb
baud = 250000 # baudrate to 25k
pclk1 = pyb.freq()[2] # = 42000000
(bs1, bs2) = (5, 8) # arbitrarily chosen
prescaler = int(pclk1 / (baud * (1 + bs1 + bs2)))
More on bit timing and frequencies
CAN: Transmit
import pyb
# Initialize CAN controller
can1 = pyb.CAN(
1, pyb.CAN.NORMAL, extframe=False,
# timing values from previous slide
prescaler=prescaler, bs1=bs1, bs2=bs2,
)
# Transmit
can1.send(b'abc', 0x100)
CAN: Receive
# Set explicit ID filter for IDs 0x100 - 0x103
can1.setfilter(
0, pyb.CAN.LIST16, 0, (0x100, 0x101 0x102, 0x103)
)
msg = can1.recv(0)
(msg_id, rtr, filter_index, data) = msg
Interrupts
External Interrupt
import pyb
import machine
def callback(i):
print("intr")
pin = machine.Pin(
'SW', machine.Pin.IN, machine.Pin.PULL_UP
)
ext = pyb.ExtInt(
pin,
pyb.ExtInt.IRQ_FALLING,
machine.Pin.PULL_UP,
callback
)
Timer Interrupt
import machine
import pyb
led = machine.Pin('LED_RED')
def toggle_led_cb(tim):
led.value(1 - led.value())
timer = pyb.Timer(1, freq=1000)
timer.counter() # get counter value
timer.freq(2) # 2 Hz
timer.callback(toggle_led_cb)
Memory Limitation
Interrupt code is run while the heap is locked;
no memory can be allocated, or de-allocated.
list.appendorset.addlist.poporset.remove- function
return - add a key to a
dict - and more
Scheduling
To work around interrupt limits.
import micropython, machine
switch = machine.Pin('SW')
timer = pyb.Timer(1, freq=2)
window = []
def populate_window(t):
global window
window = window[-9:] + [switch.value() == 0]
timer.callback(populate_window) # BAD! raises MemoryError
def timer_callback(t):
micropython.schedule(populate_window, t)
timer.callback(timer_callback)
Your Script
Boot Order
- SD Card -
/sd/main.py - Flash -
/flash/main.py
Both can be copied to via USB Mass Storage.
The red LED will illuminate while
the device is busy.
Programs on SD cards alows a sort of nostalgic cartridge system.
Import Path
Defaults are...
>>> import usys as sys
>>> sys.path
['', '/sd', '/sd/lib', '/flash', '/flash/lib']
Installing from PyPI
- Download
.tar.gzfile - Extract to one of the
libfolders
For Example...
Installingitertools.
- Download
itertoolsfrom PyPI - Extract to
libon the sd card - result should look like:
examples/itertools-installed
Debugging
+ Bug
Let's run a main.py with a bug.
import pyb
led = pyb.LED(1) # Red LED
sw = pyb.Switch()
while True:
time.sleep(0.05)
if sw.value():
led.on()
else:
led.off()
You want a hint? I don't have time.
Use a REPL
Read output fromMicroPython interpreter.
- connect the board to a
REPL - soft reset the board with
Ctrl+D - read the output
The Result
Ctrl+D is pressed...
>>>
PYB: sync filesystems
PYB: soft reboot
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "main.py", line 7, in <module>
NameError: name 'time' is not defined
MicroPython v1.9.2 on 2017-08-23; PYBv1.1 with STM32F405RG
Type "help()" for more information.
>>>
time is on line 7.
Debugging Interrupts
To enable standard exception reporting to a REPL
import micropython
micropython.alloc_emergency_exception_buf(100)
alloc_emergency_exception_buf
documentation for details.
Debugging with pdb?
Not yet, sadly.
Watch this space , and #3009 .
Asyncio
Multitasking
For example...
- Toggle red LED every 1000 ms
- Toggle green LED every 450 ms
The confusing way
Without usingasyncio
import utime as time
from machine import Pin
led1, t1 = Pin('LED_RED', Pin.OUT), time.ticks_ms()
led2, t2 = Pin('LED_GREEN', Pin.OUT), time.ticks_ms()
while True:
if time.ticks_diff(time.ticks_ms(), t1) >= 1000:
t1 = time.ticks_ms()
led1.value(1 - led1.value())
if time.ticks_diff(time.ticks_ms(), t2) >= 450:
t2 = time.ticks_ms()
led2.value(1 - led2.value())
time.sleep_ms(10)
The asynchronous way
import uasyncio as asyncio
from machine import Pin
async def blink(led, period):
"""Toggle LED once each period"""
while True:
await asyncio.sleep_ms(period)
led.value(1 - led.value())
# Create loop, add tasks, and run
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
loop.create_task(blink(Pin('LED_RED', Pin.OUT), 1000))
loop.create_task(blink(Pin('LED_GREEN', Pin.OUT), 450))
loop.run_forever()
LCD Interface
LCD160CRv1.0
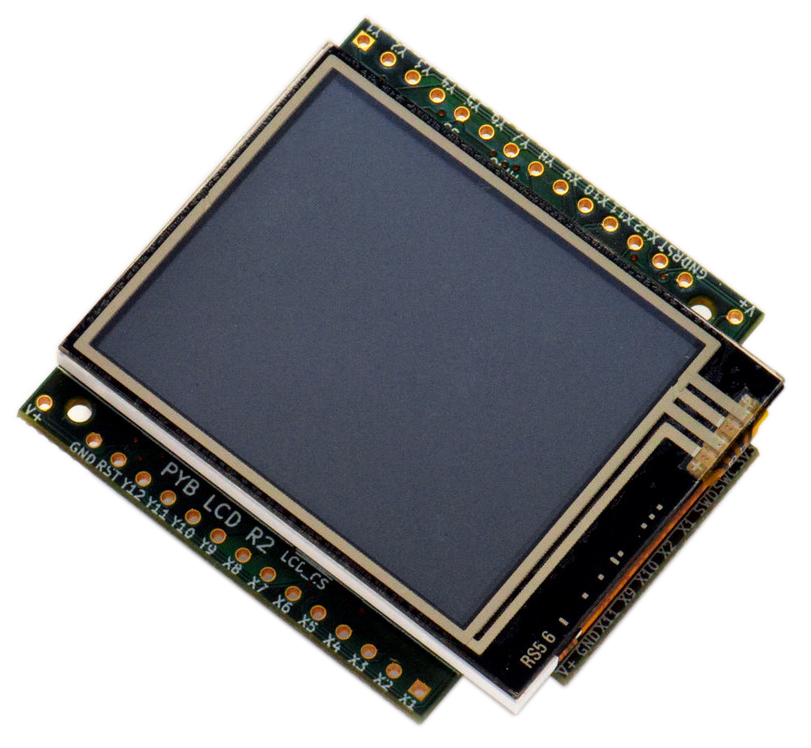
- Resolution: 160 x 128
- Colour: 16-bit (565)
- Screen refresh: 30fps
- Resistive Touch
- store + references
- demo video
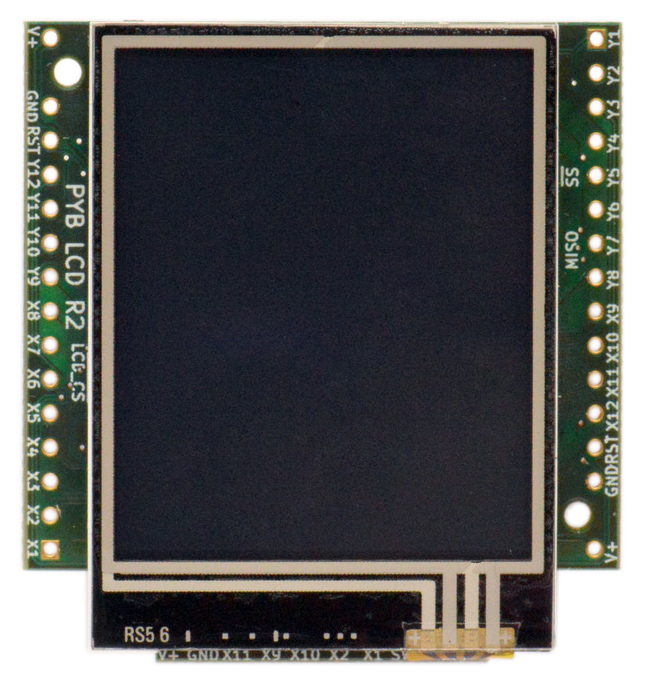
Wiring
pyboard Right >> LCD Left
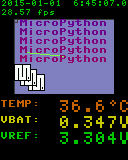
Run Test
Thelcd160cr & lcd160cr_test
modules are included with pyboard's MicroPython build.
import lcd160cr
import lcd160cr_test
# Create LCD object
lcd = lcd160cr.LCD160CR('XY')
# Run built-in test on lcd
lcd160cr_test.test_features(lcd)
lcd160cr_test.test_mandel(lcd)
Tests results
Lines
import lcd160cr
lcd = lcd160cr.LCD160CR('XY')
# white on black
lcd.set_pen(0xffff, 0)
lcd.erase() # clear screen
# Draw a line
lcd.line(0, 0, lcd.w, lcd.h)

Poly Lines
from math import sin, cos, pi
x = int(lcd.w / 2)
y = int(lcd.h / 2)
points = []
for i in range(6):
a = i * (0.8 * pi)
points += [
x + int(60 * sin(a)),
y + int(60 * cos(a))
]
lcd.poly_line(
bytearray(points)
)

Boxes
# Set some colours
BLUE = lcd.rgb(0, 0, 255)
YELLOW = lcd.rgb(255, 255, 0)
GREY_20 = lcd.rgb(51, 51, 51)
lcd.set_pen(0, GREY_20)
lcd.erase()
lcd.set_pen(BLUE, YELLOW)
lcd.rect(10, 10, 100, 70)
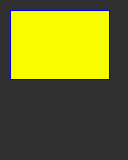
Text
# Set some colours
WHITE = lcd.rgb(255, 255, 255)
GREEN = lcd.rgb(0, 255, 0)
lcd.set_pen(WHITE, 0)
lcd.set_text_color(GREEN, 0)
for i in [1, 2, 3, 4]:
# normal
lcd.set_pos(10, i * 25)
lcd.set_font(i, scale=0)
lcd.write('Font%i' % i)
# scaled up by 1
lcd.set_pos(80, i * 25)
lcd.set_font(i, scale=1)
lcd.write('f%i' % i)
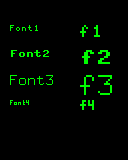
JPG
Pre-process jpg:
sudo apt install libjpeg-progs
jpegtran orig.jpg > photo.jpg
pyboard code:
fname = '/sd/images/photo.jpg'
with open(fname, 'rb') as f:
buf = bytearray(f.read())
lcd.set_pos(0, 0)
lcd.jpeg(buf)

Resistive Touch
(touching, x, y) = lcd.get_touch()
# touching: is True or False
# x: int coord of most recent touch
# y: int coord of most recent touch
And More
- Frame buffering
- Window scrolling
- Portrait / Landscape coordinates
- Backlight brightness
- Save settings to flash
Documentation here.

